Your junk mail settings move emails perceived as undesirable to the Spam folder. Filters work a bit like this, except that you get to decide which emails are matched, and what happens to them! Filters in your Rackspace email account can be used to automatically move messages to a specific folder, delete a matching email, or forward it to a different email address. (To redirect all your emails to another account, you should enable mail forwarding instead!)
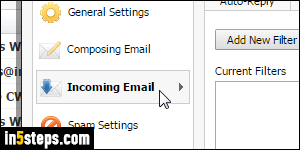
To configure your filters, click on the menu button in the top right corner of the page ("hamburger" icon, with three horizontal bars - previous screenshot), and select Settings. Then, click on the "Incoming Email" options on the left.
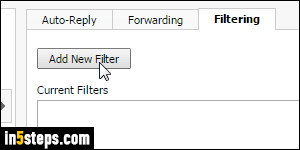
Select the Filtering tab at the top, and click on Add New Filter. When the Add Email Filter popup opens, type a meaningful name for your filter in the text box: make it clear enough so you still remember what it does in six months!
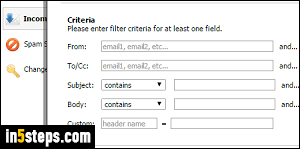
Now enter your Criteria (what some email programs / webmail providers call Conditions). These are additive rules: all conditions must be met, not just one or the other. To filter by sender, enter an email address in the From box; to filter by recipient, type an address in the To/Cc text box. To match words in the body or subject line, type them (in order) in each text field. Notice that the dropdowns let you match by "contains", "doesn't contain", and "begins with".
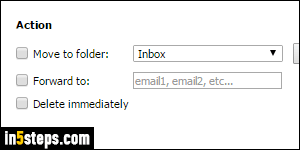
Now select your Action: what should happen to a message that matched all these conditions? Check Move to folder to do so, and select an existing folder or create a new one; Forward to one or more email addresses (separated by commas) that you enter in the text box; or Delete immediately to move that email to the Trash folder. Click Save to create your filter! This only affects mail you receive from now on: no existing message will be moved / deleted / etc.
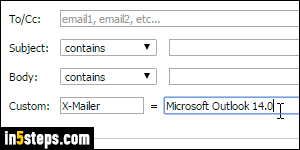
Bonus Tip - Matching custom email headers!
Unlike any webmail provider I can recall, Rackspace lets you filter by matching email headers. This metadata "travels" with any message you send or receive. You could, for example, match emails sent from Microsoft Outlook by targeting the X-Mailer header, X-Originating-Ip to match IP addresses, etc.